Restaurant Acoustics: Why They Matter
- Dec 5, 2025
A loud, bustling restaurant is a good thing...until it isn't. If a restaurant or bar gets too loud, it can negatively impact the dining experience for customers and also make it difficult for front-of-house staff to do their job.
Why are Good Acoustics Important in a Restaurant?
Multiple studies and surveys have shown that when noise levels are too loud in a restaurant, customers are more likely to leave early and not return. Additionally, a 2016 survey from Zagat found "noise" to be the second most irritating thing about dining out.
What Causes Bad Acoustics in a Restaurant?
Obviously, restaurants can get quite loud due to conversation, live music, and the clanking of dishes and silverware. But the very aesthetics of many modern restaurant spaces also contribute to these acoustic issues: low-maintenance but highly reflective hard surfaces are popular right now – that means no carpeted floors or upholstered furniture to help absorb sound. Open dining rooms (and open kitchens) where sound travels freely without partitions or walls to get in its way add to the noise issues.
How Do I Fix Poor Sound Quality in a Restaurant?
There's a few simple ways to address sound issues in a restaurant:
- Incorporate background music or sound emitters. When played at a low level, they can help to mask unwanted noise.
- Add soft furnishings such as couches or curtains to help absorb sound.
- Experiment with different layouts. If a particularly "hot" corner of the dining room seems to trap sound, for instance, consider removing tables from that area.
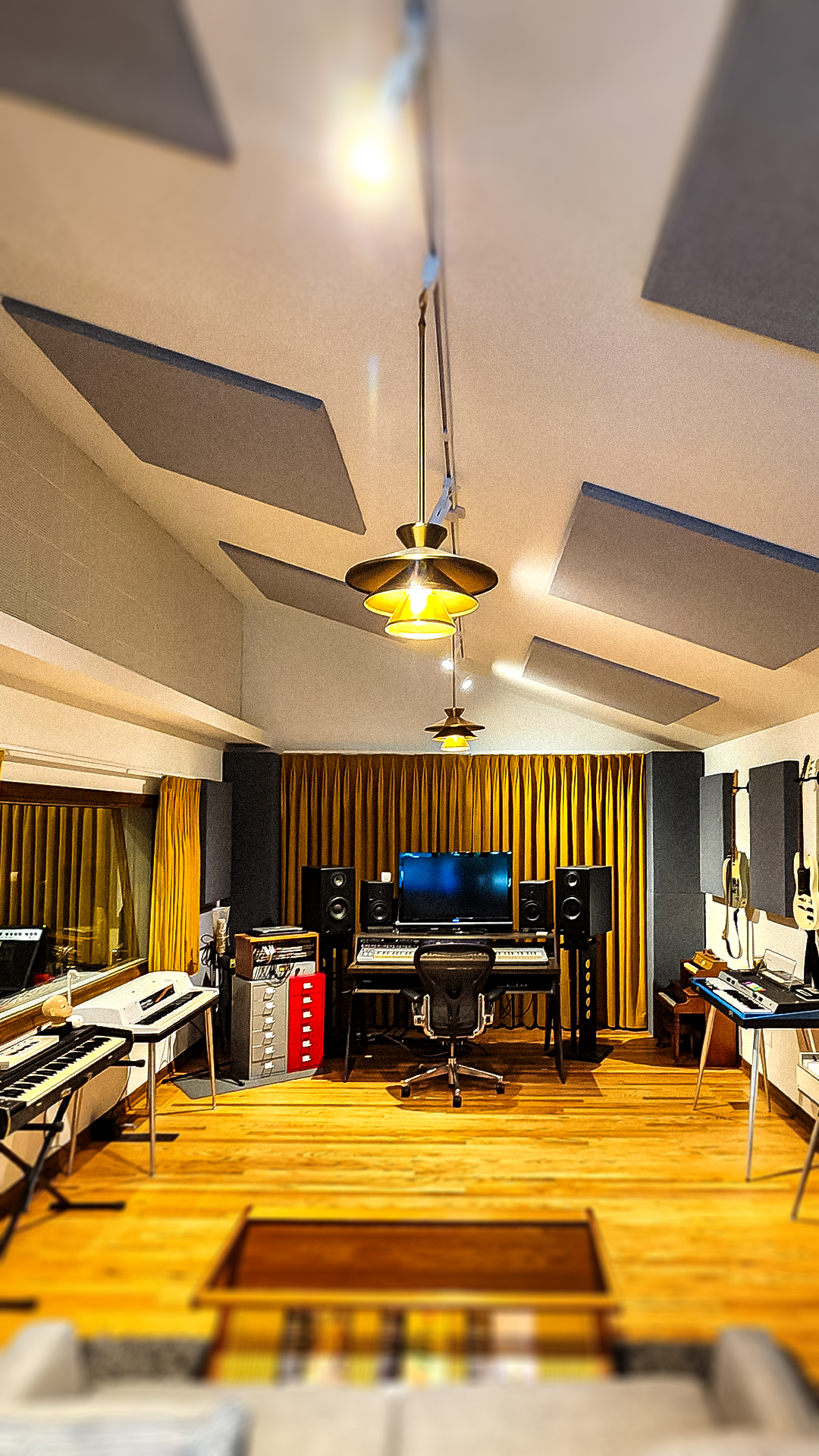
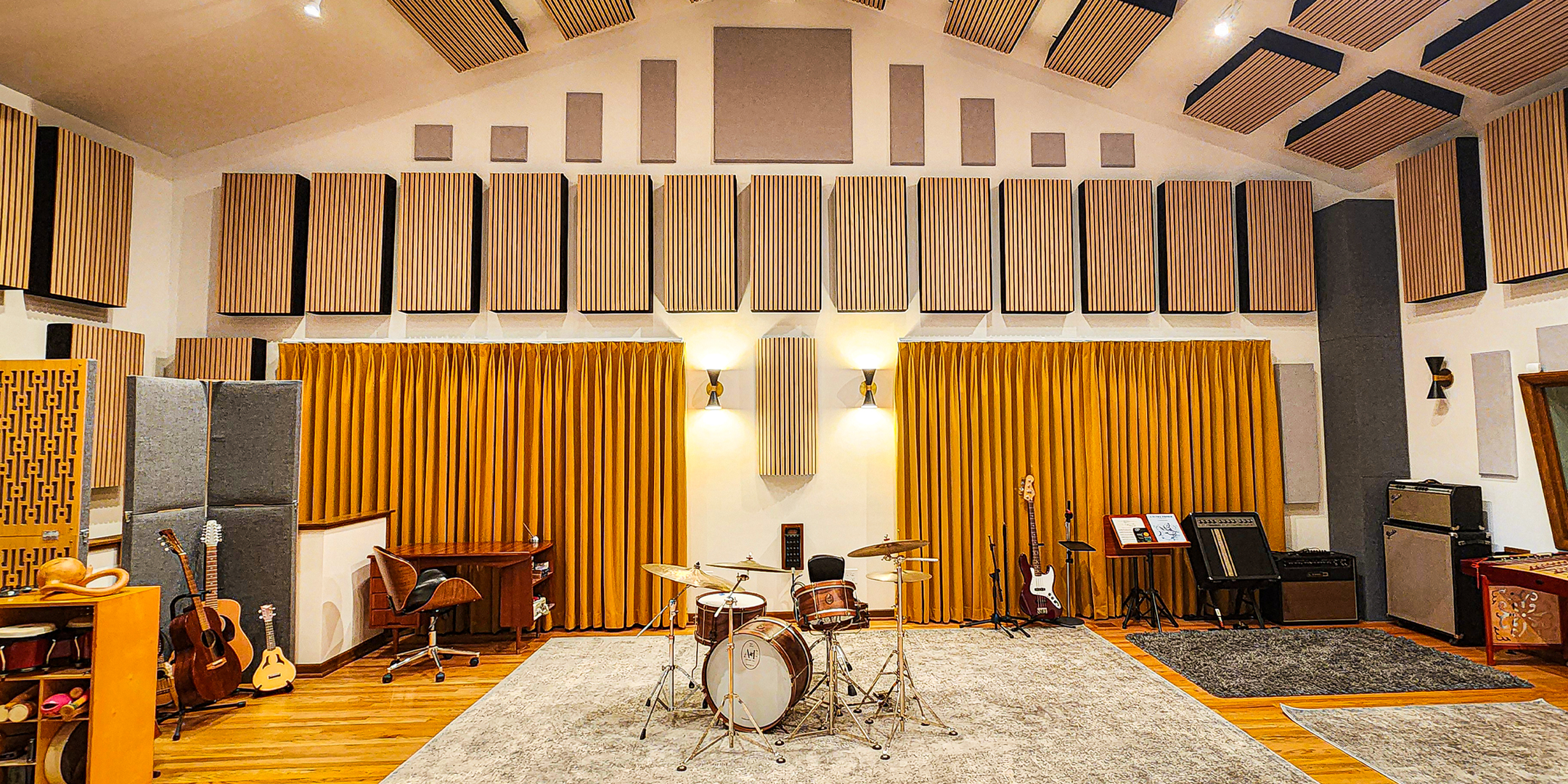
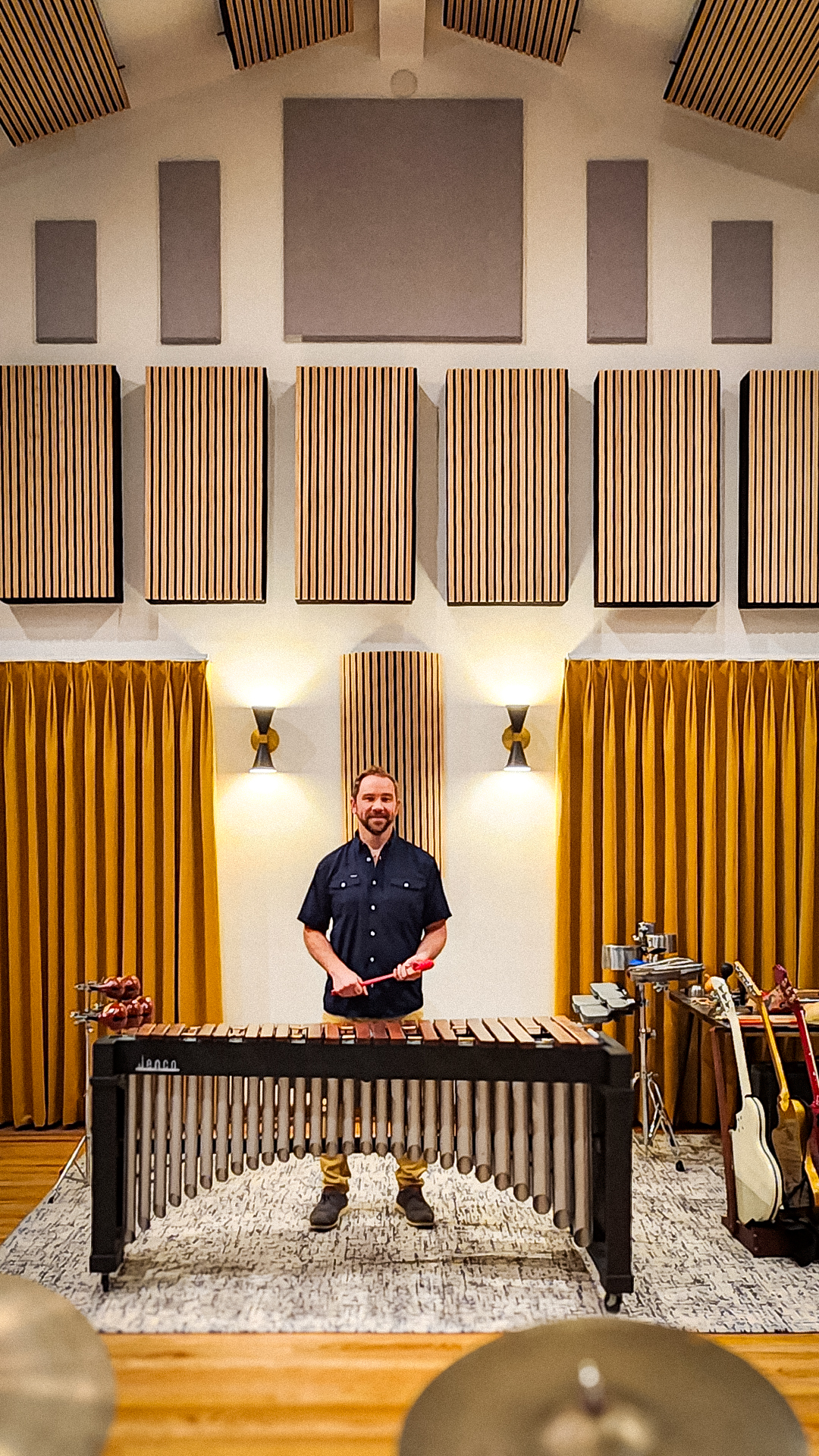
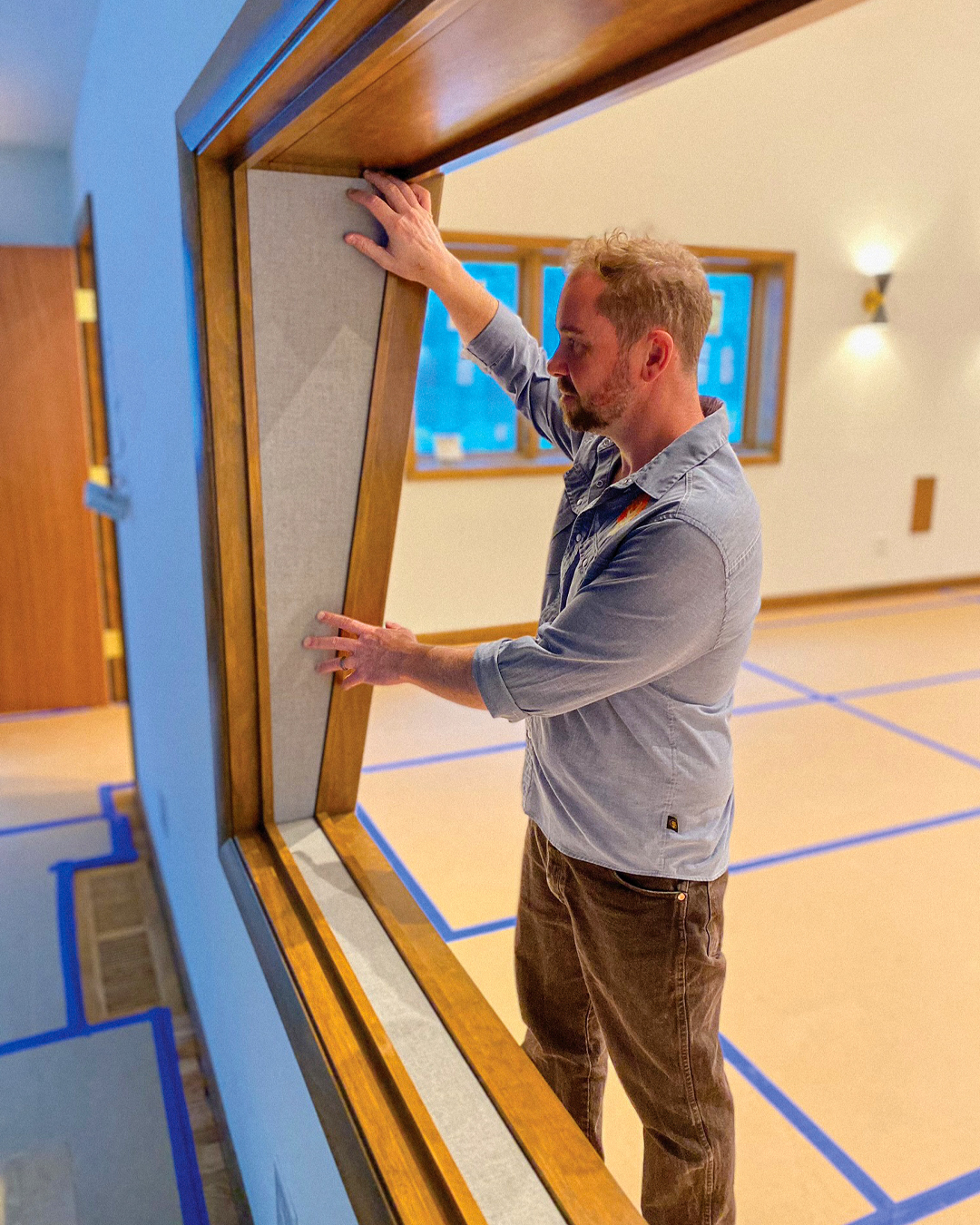
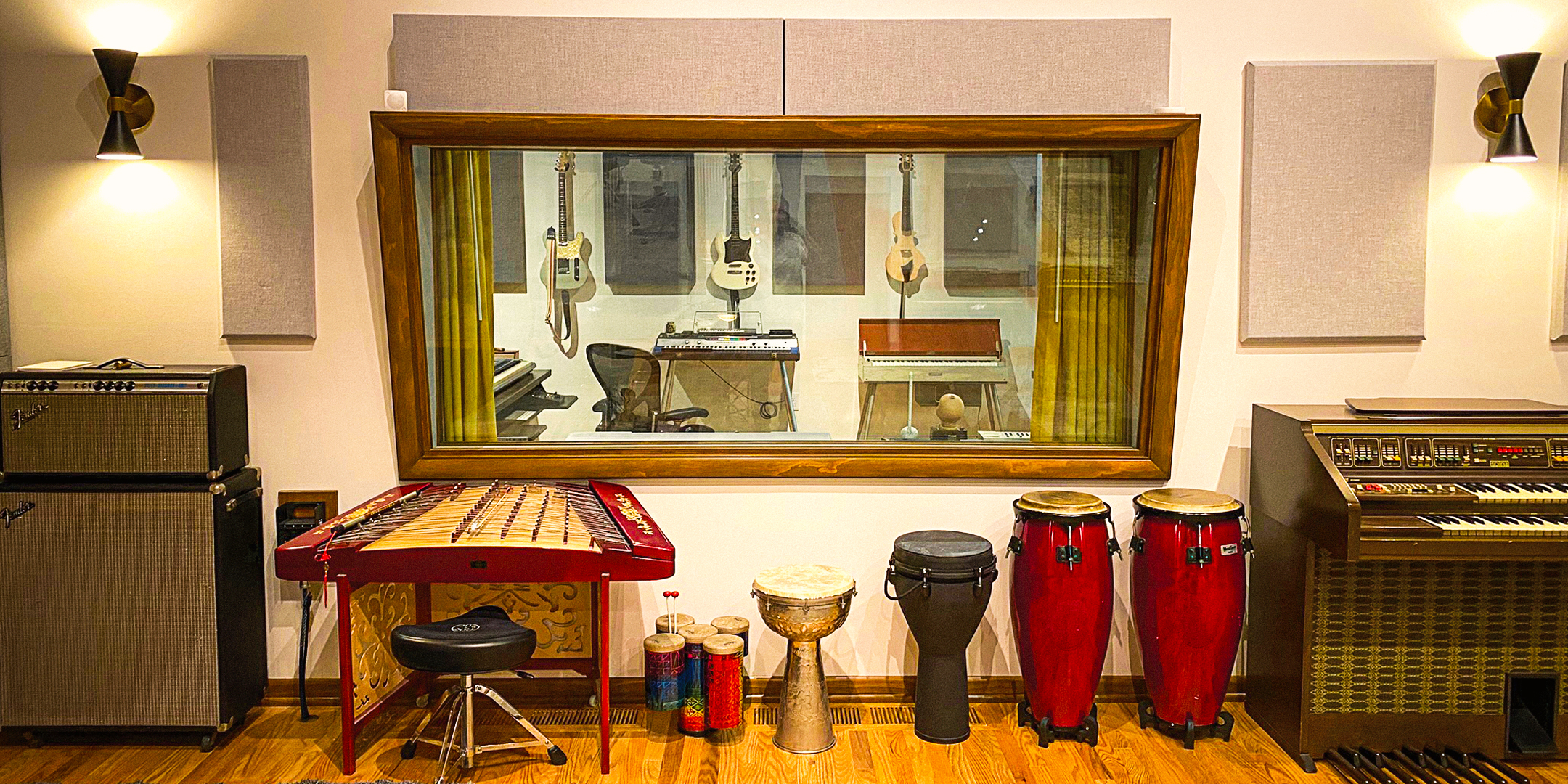
Sound-absorbing acoustic panels like ones made by Audimute can absorb up to 95% of the echoes, reverberations, and mid to high frequencies they come into contact with.
Which Audimute Acoustic Panels are Best for a Restaurant?
Restaurant owners have several Audimute options for sound-absorbing solutions:
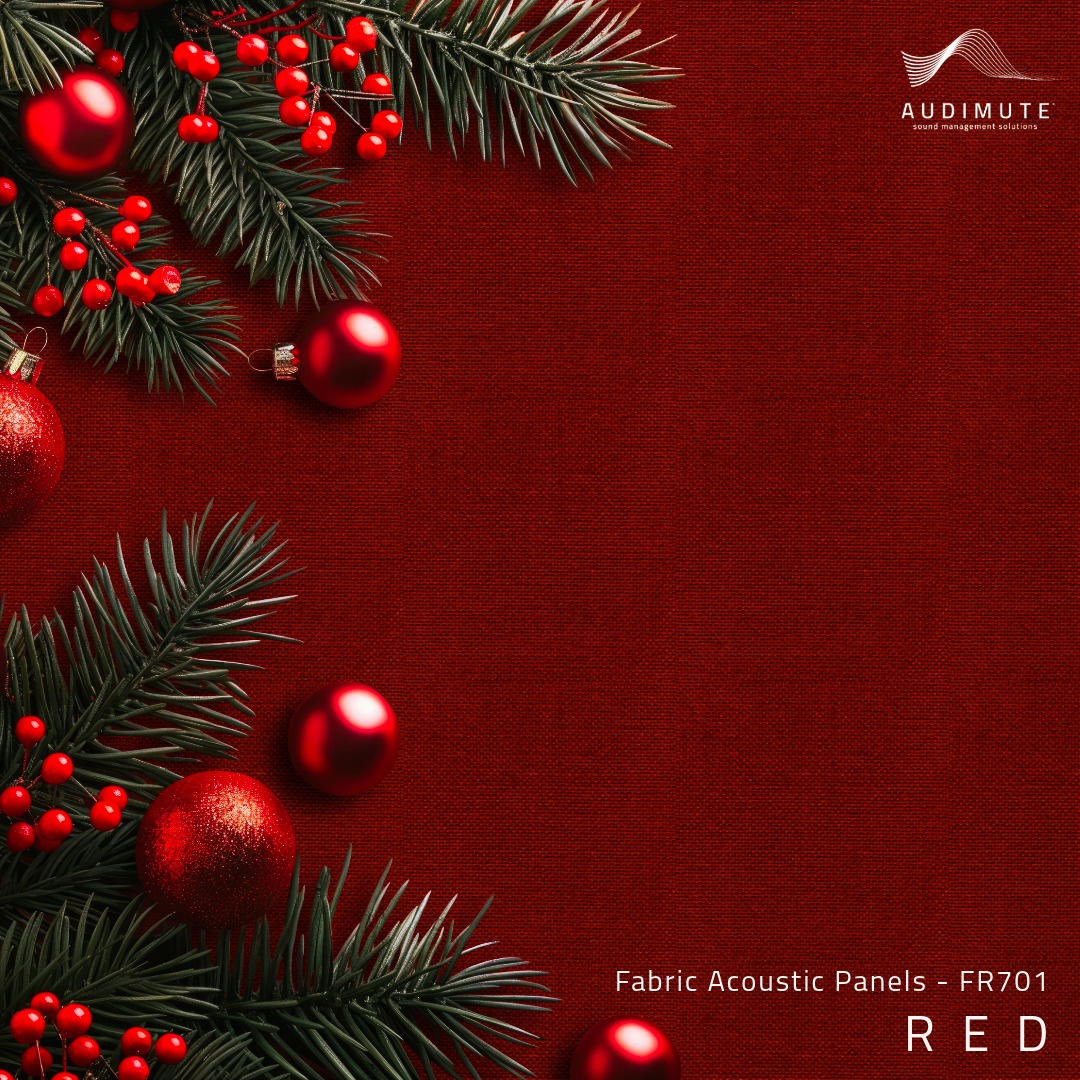
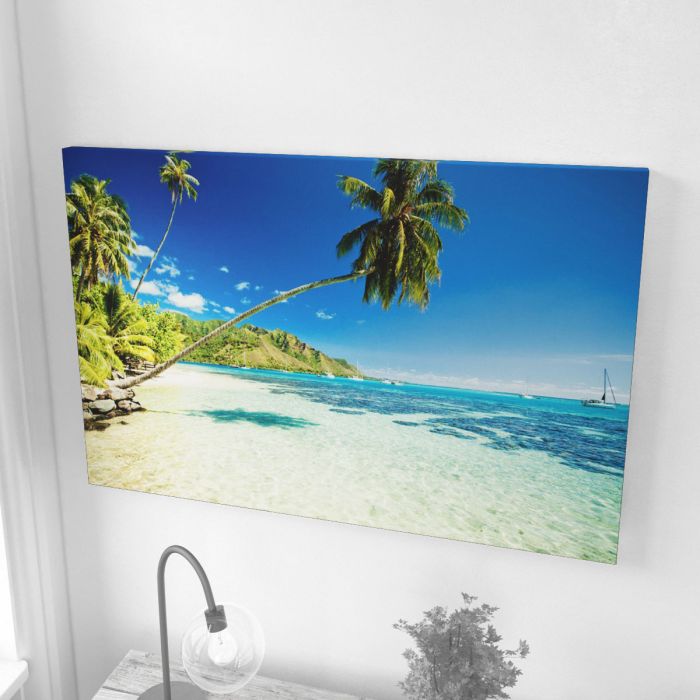
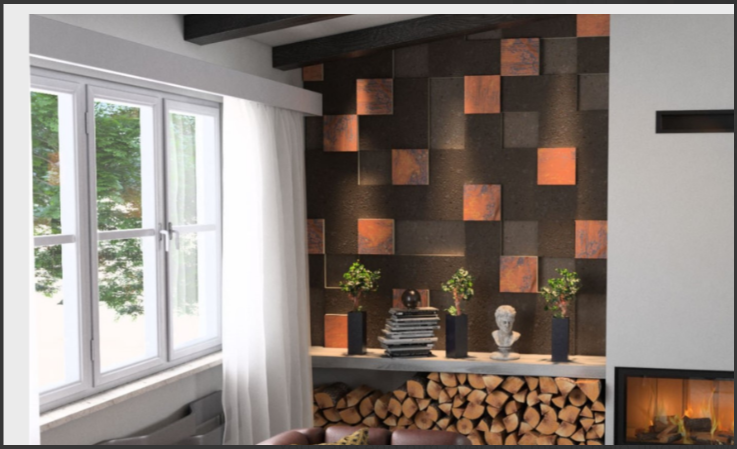
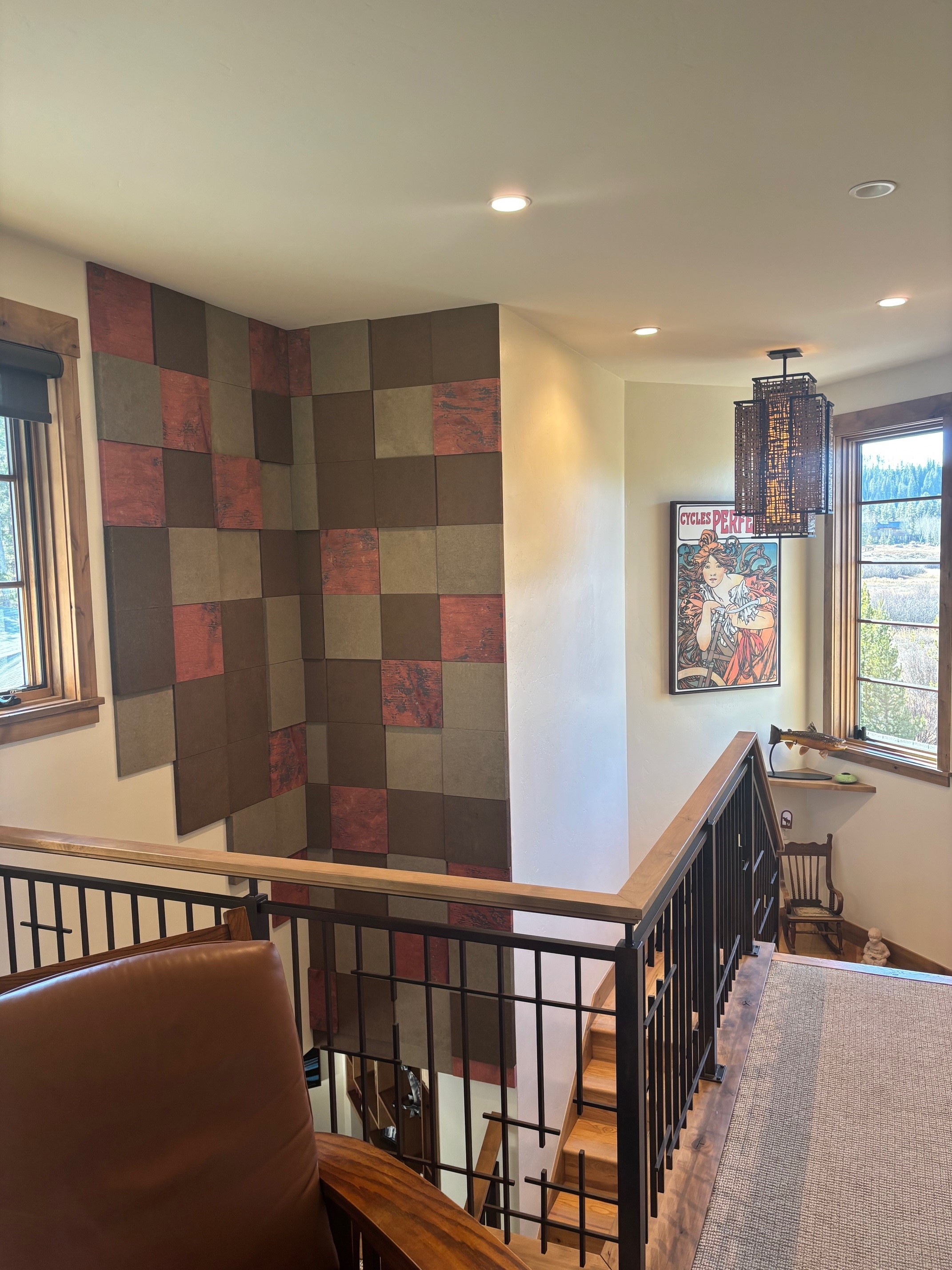
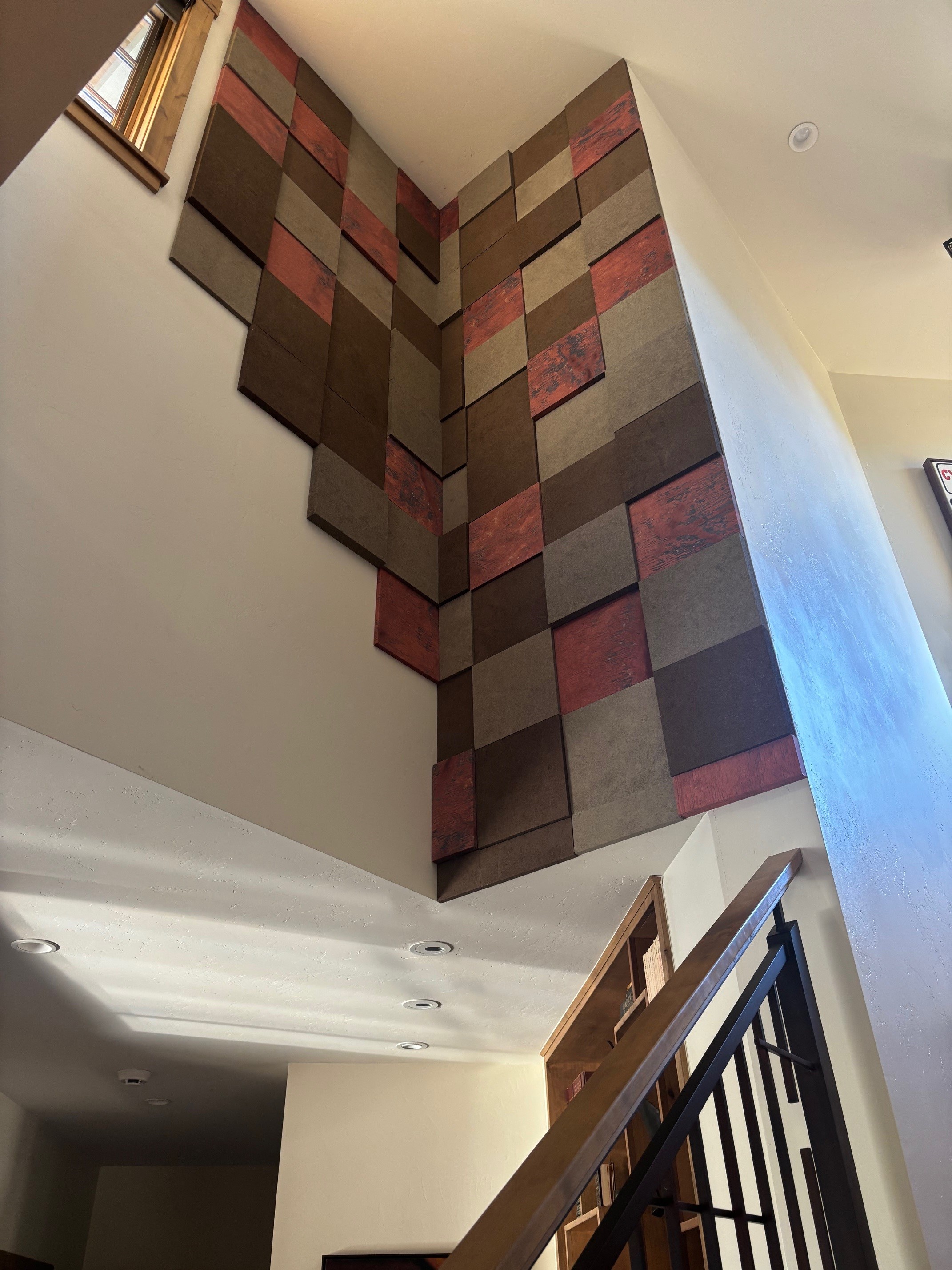
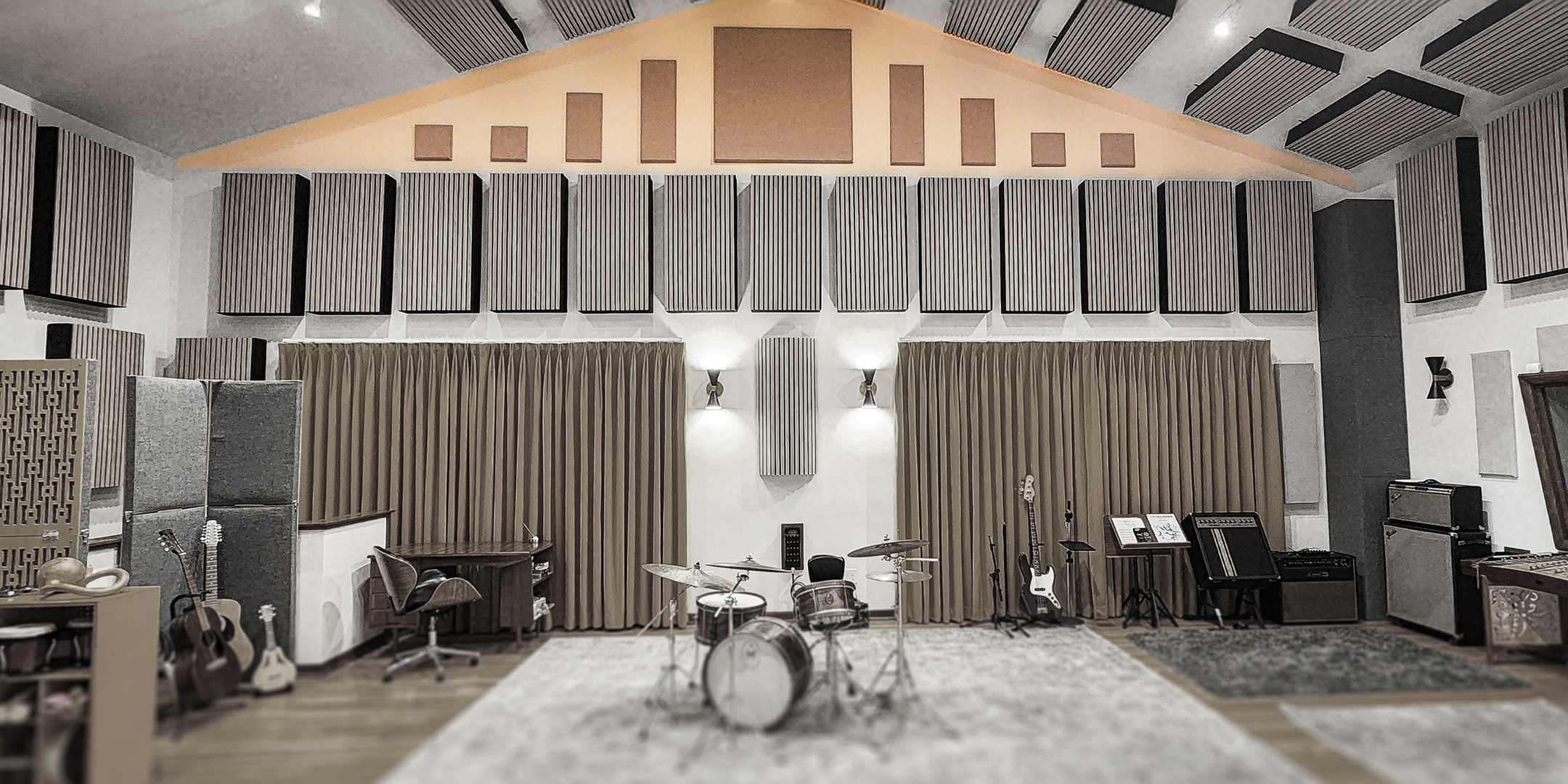
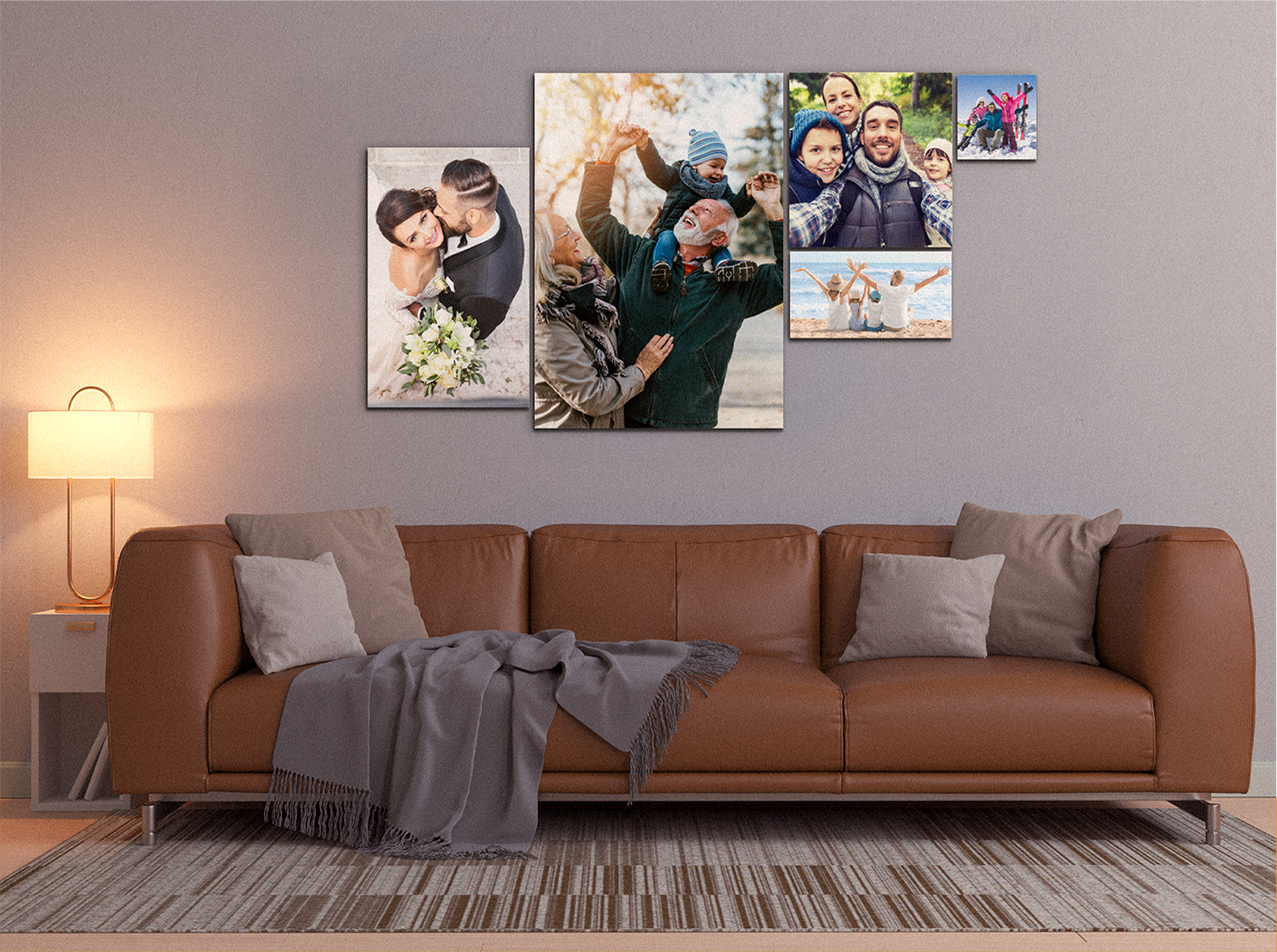
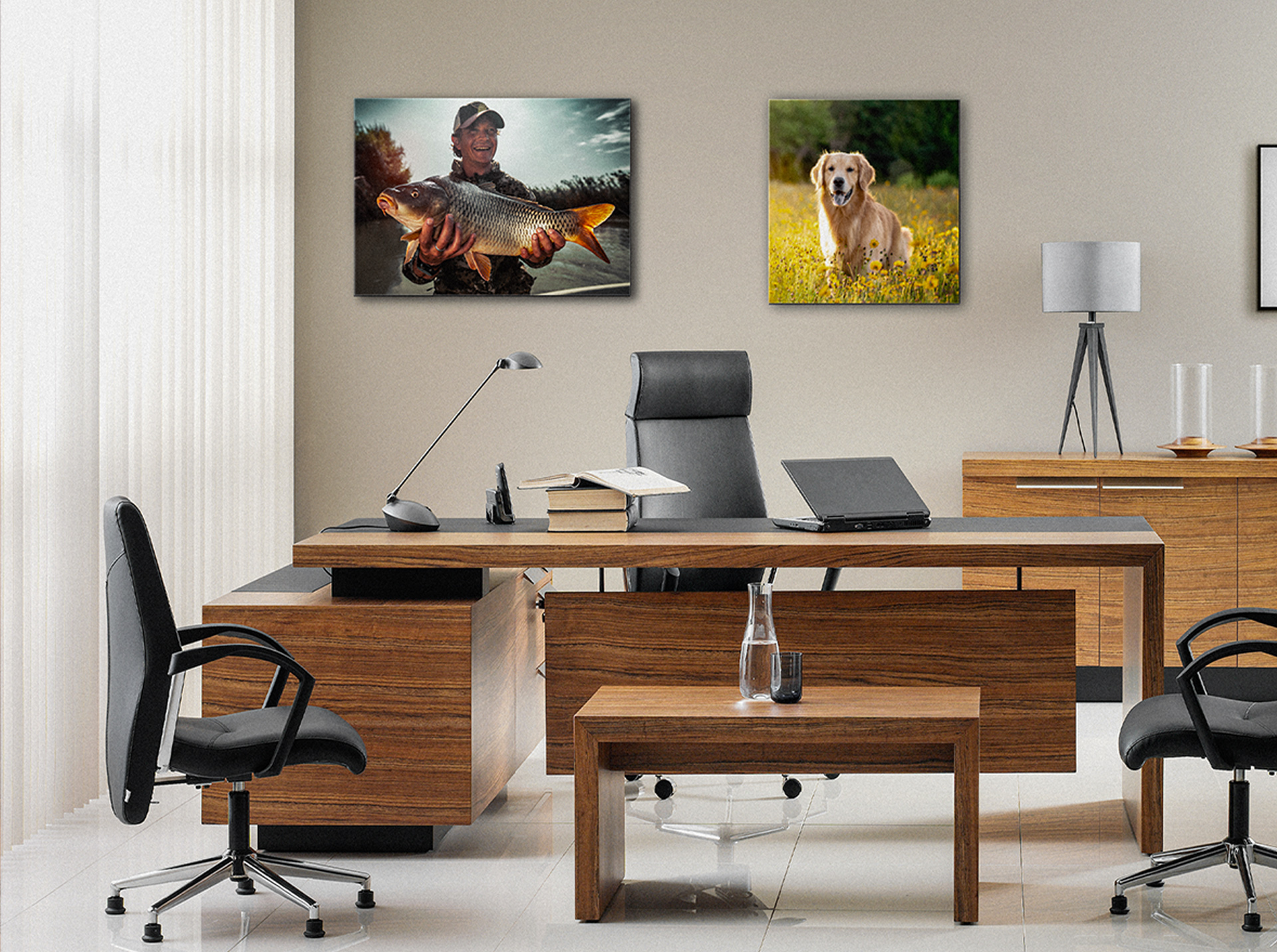
- Fabric Acoustic Panels are durable, elegant, and can easily be cleaned. They're excellent for high-traffic areas like dining rooms or waiting areas.
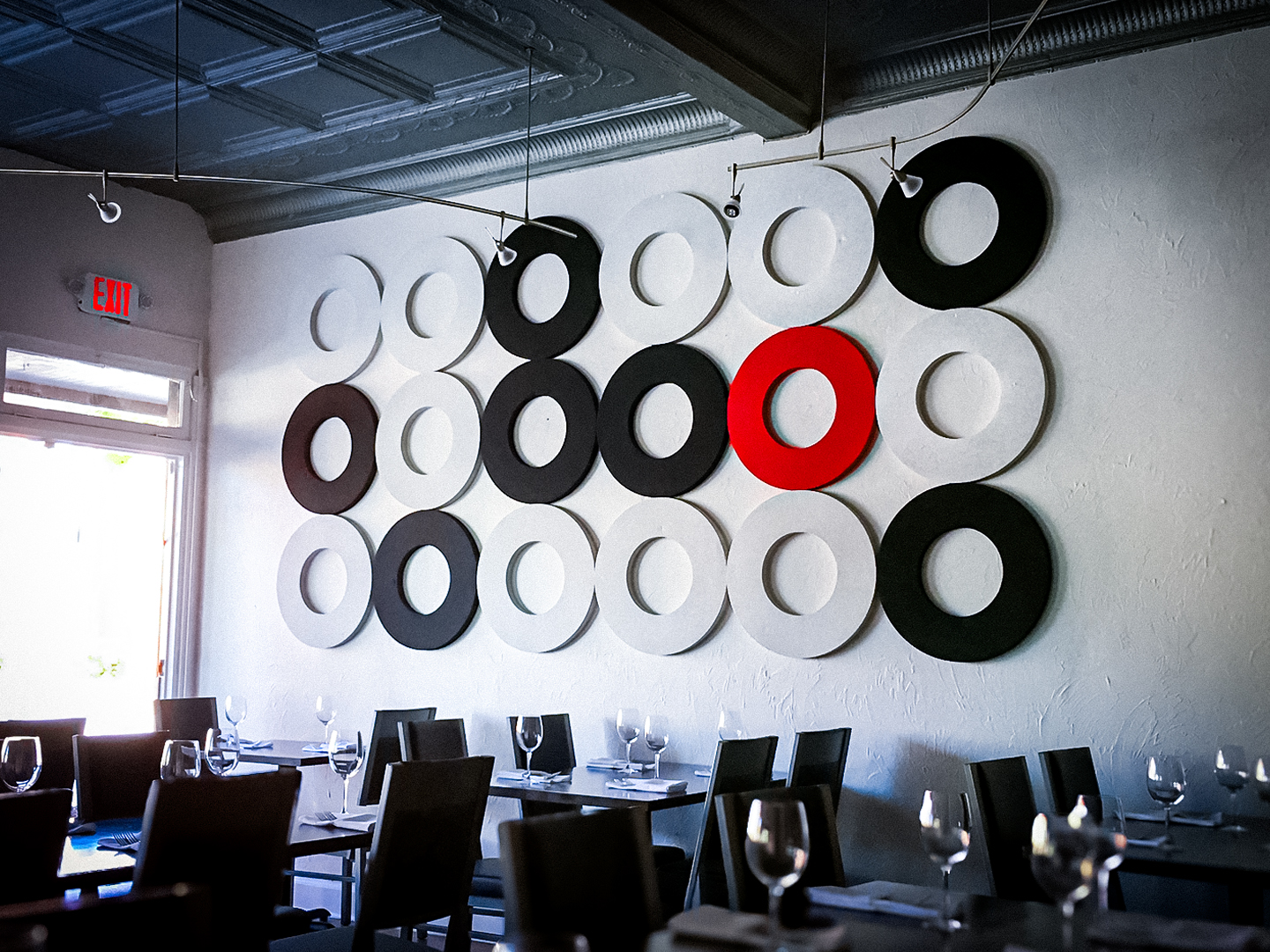
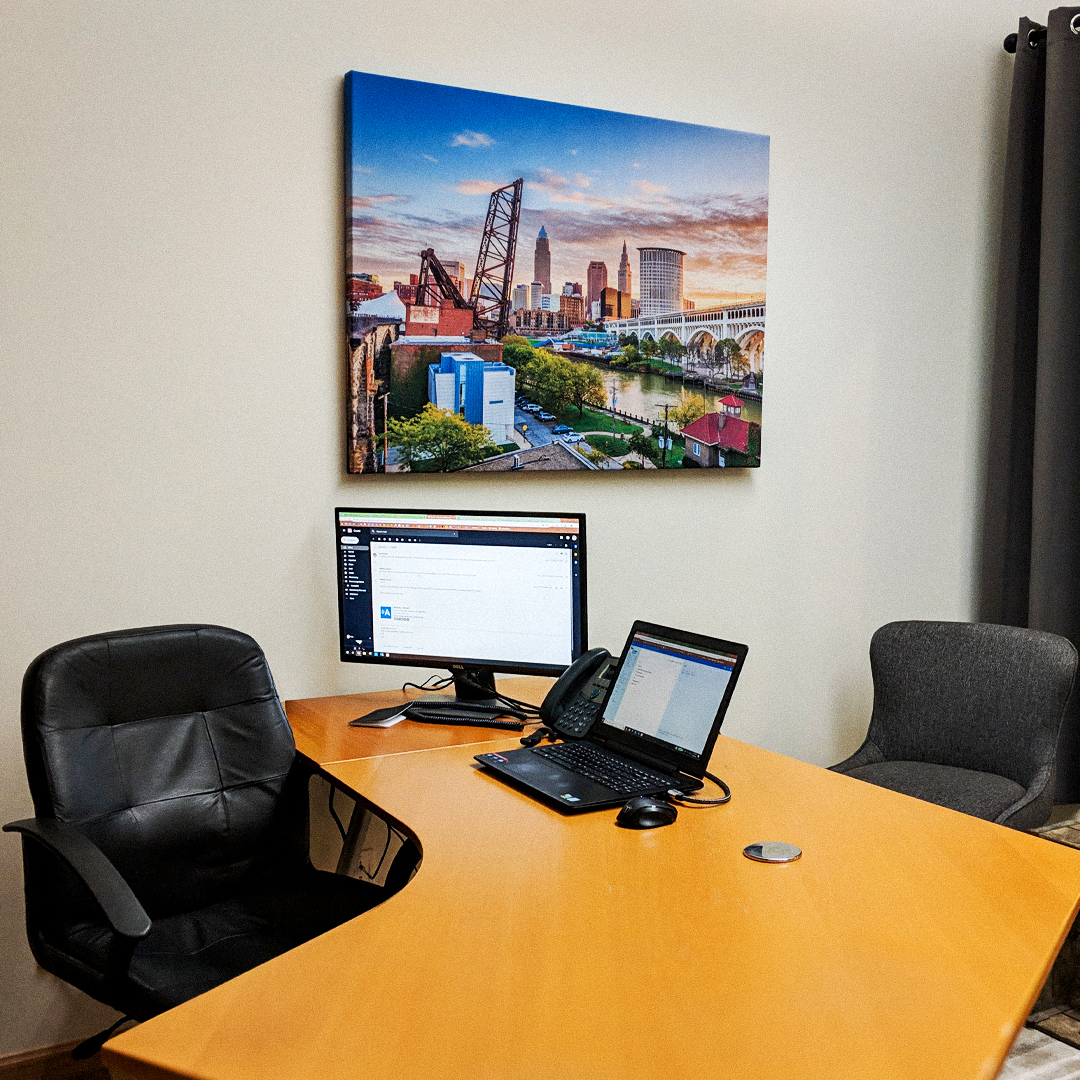
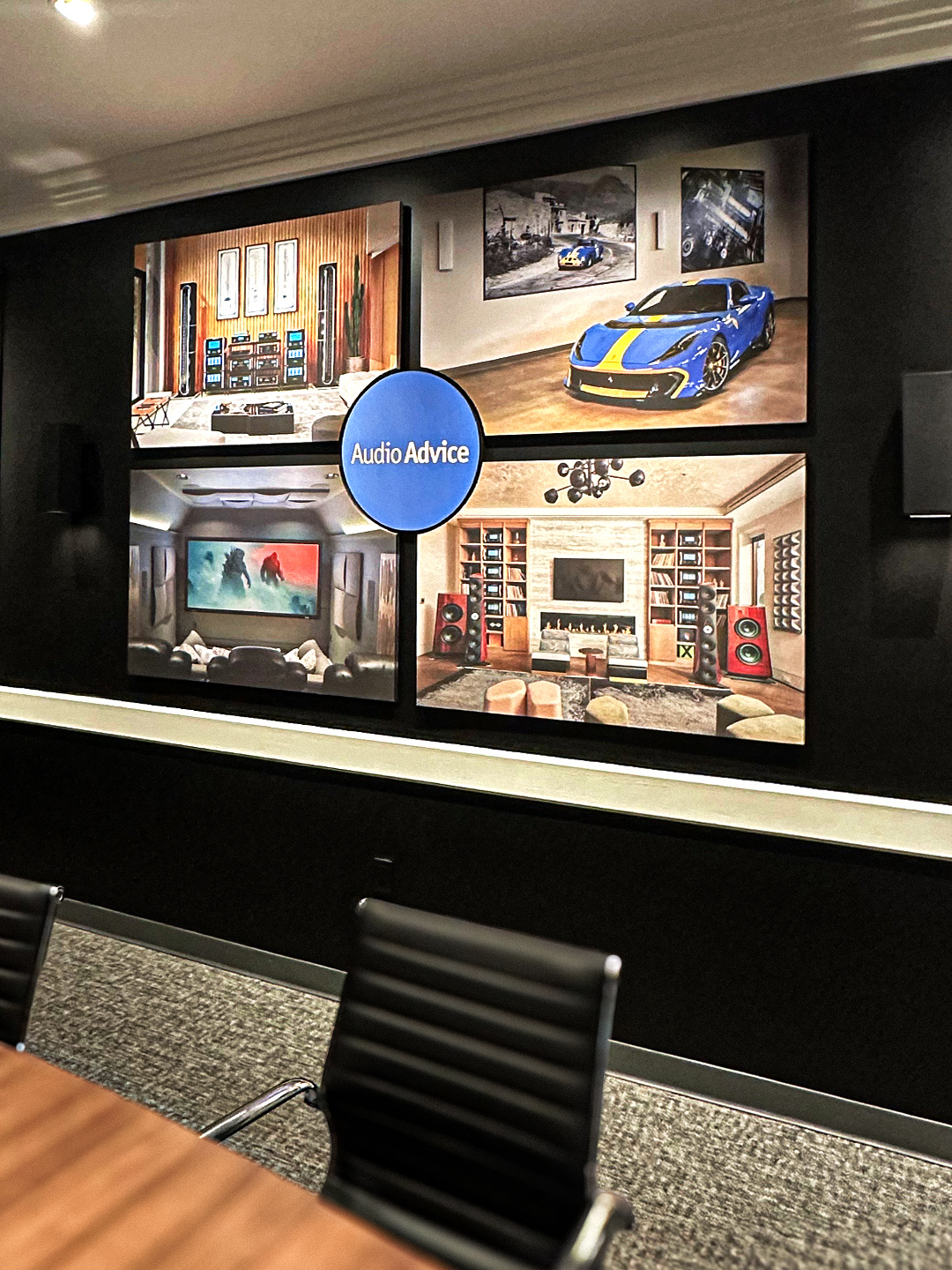
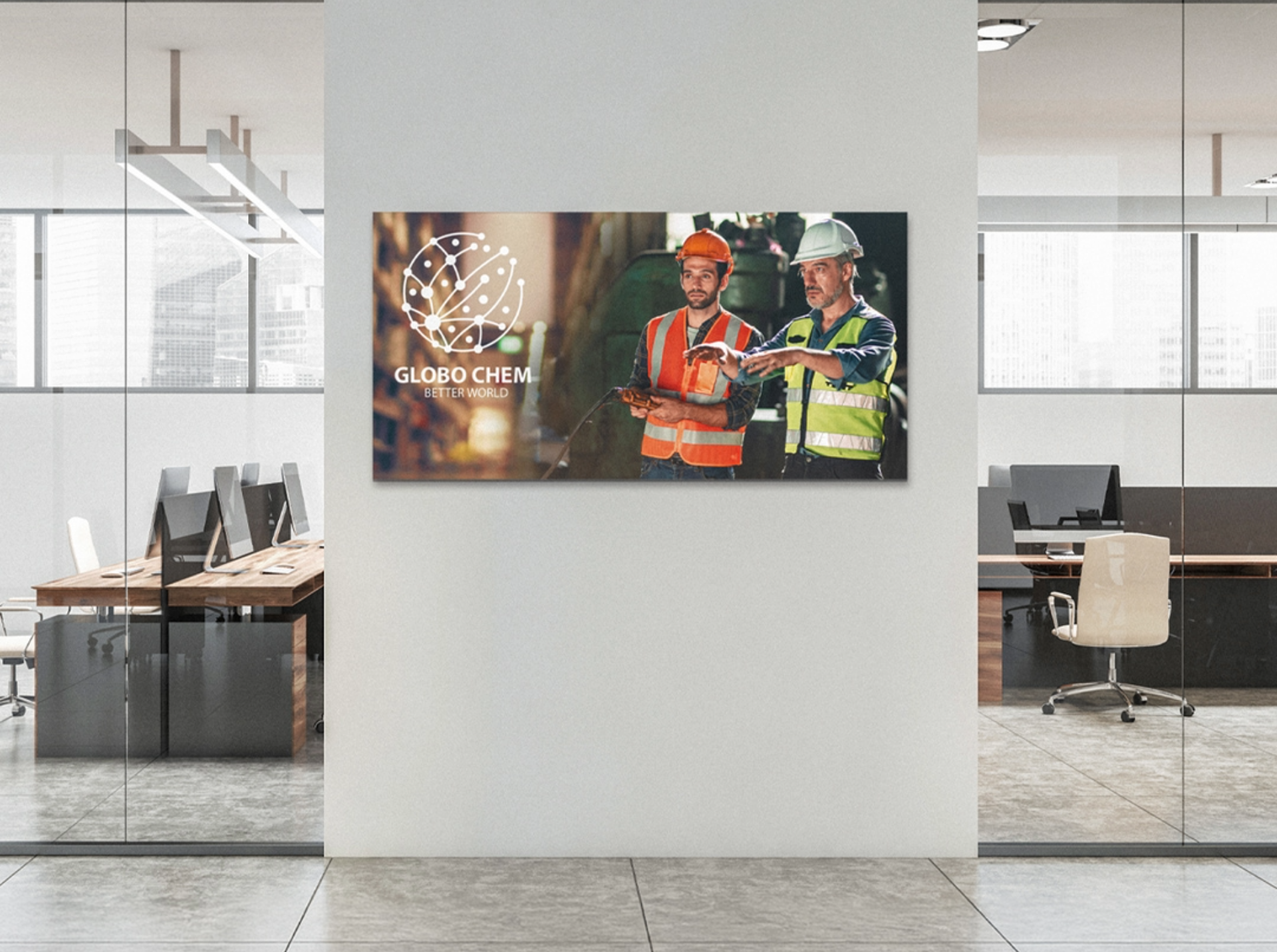
- Acoustic Image Panels are a great way to incorporate branding into your acoustic treatment. They can be customized with logos, top menu options, or other elements of brand identity.
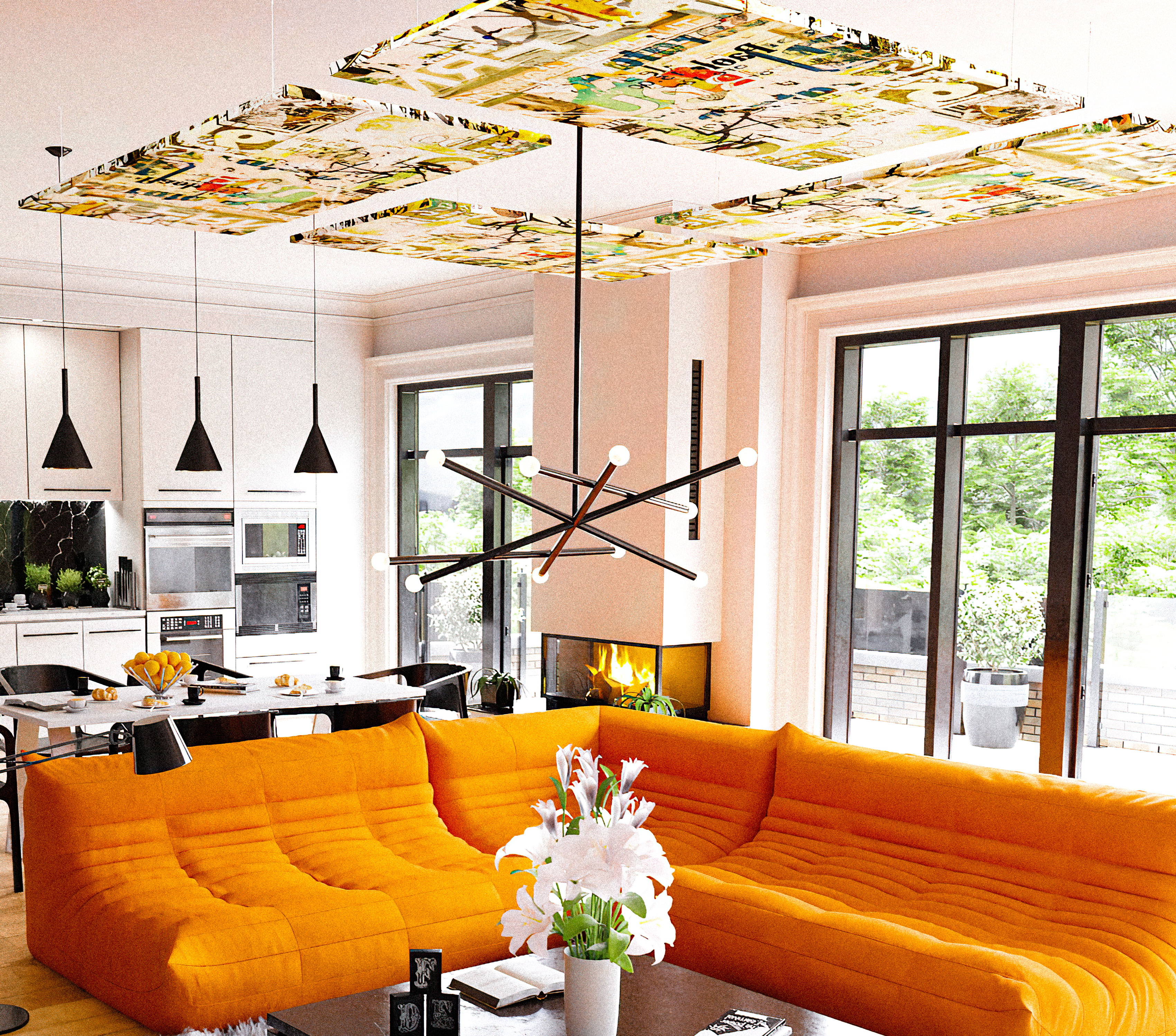
- Acoustic Ceiling Clouds and Baffles are perfect for restaurants with limited wall space or high ceilings. They can be suspended to absorb sounds from above.
- AcoustiColor® Acoustic Direct Mount Ceiling Tiles are particularly popular in the hospitality industry. They can be coated to match any color from Sherwin-Williams, allowing them to blend in with ceilings.
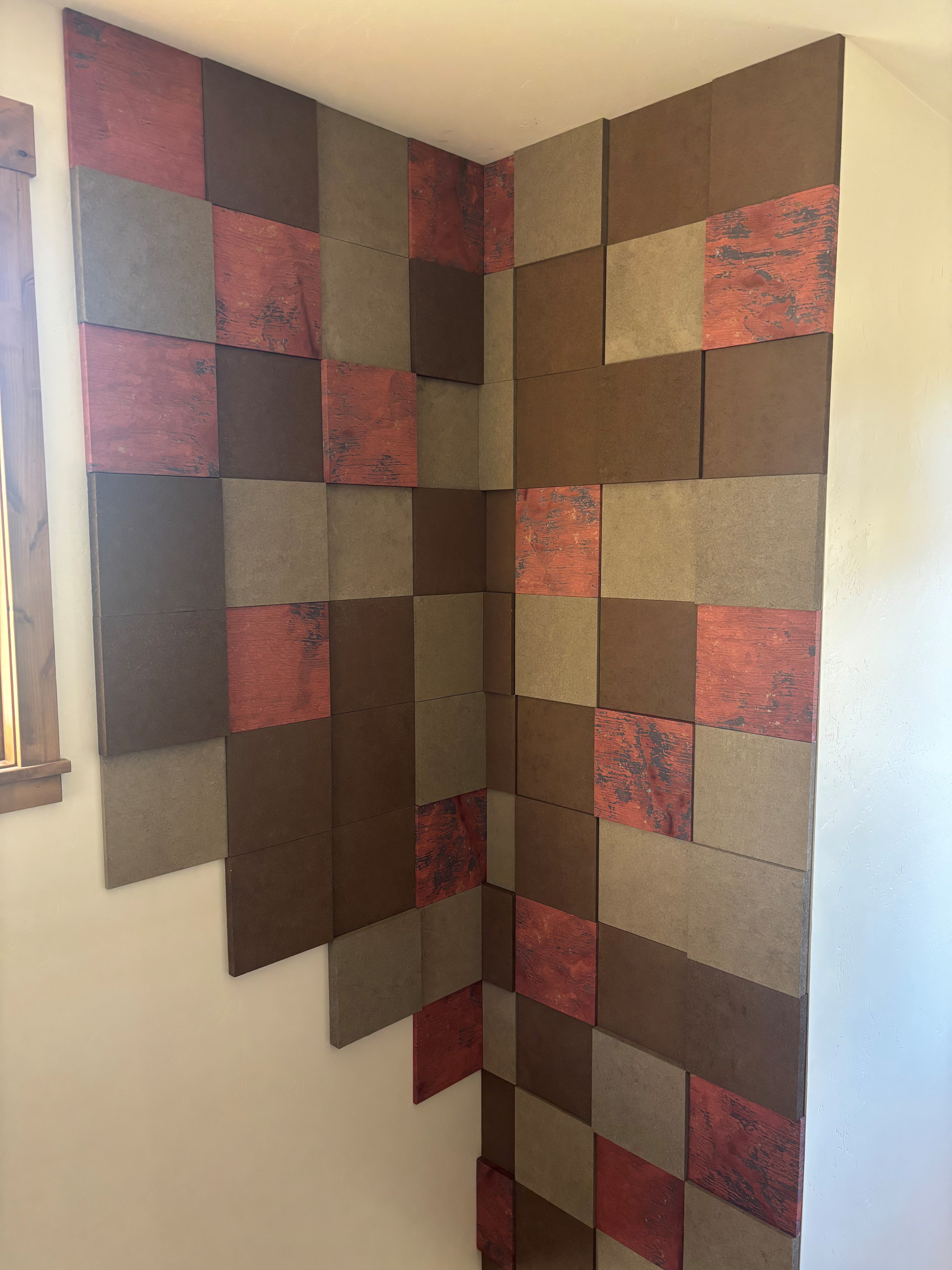
- Audimute Strata® is also popular due to its flexible nature. It can be contorted to fit curved walls or other areas with unusual angles to provide sound absorption in a visually appealing design.